Effective Production Management. Process elements, methods, and benefits of implementing a system
The primary goal of effective production management is to maximize company profits by optimizing the entire manufacturing process. It’s not just about making a product; it’s about planning so that goods meet customer specifications and deadlines while strictly optimizing resources (machines, time, and human labor).
Implementing a structured system allows companies to reduce costs, shorten order fulfillment times, and eliminate waste (such as overproduction or excess inventory). This approach is essential for increasing competitiveness and building a strong brand.

Effective production management increases a company’s profits, which in turn is the primary goal of every manufacturing enterprise.
Product management is the business process of planning, developing, launching, and managing a product or service. It includes the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation to development to go to market. (quoted from Wikipedia)
Expanding this definition, one can say that production management involves planning all processes in such a way that goods comply with specifications, meet customer needs, are produced in the required quantity and within the expected timeframe, while optimally using all available resources – including machines, time, and human labor.
Table of contents:
- Production Management – Process Elements
- Production Management – Stages
- Production Management – Methods
- Lean-based production management system – benefits for the company
- Implementation outcomes
Production Management – Process Elements
Production management can be compared to a complex network of dependencies, where every element matters and influences the next. Therefore, the literature distinguishes several key subprocesses:
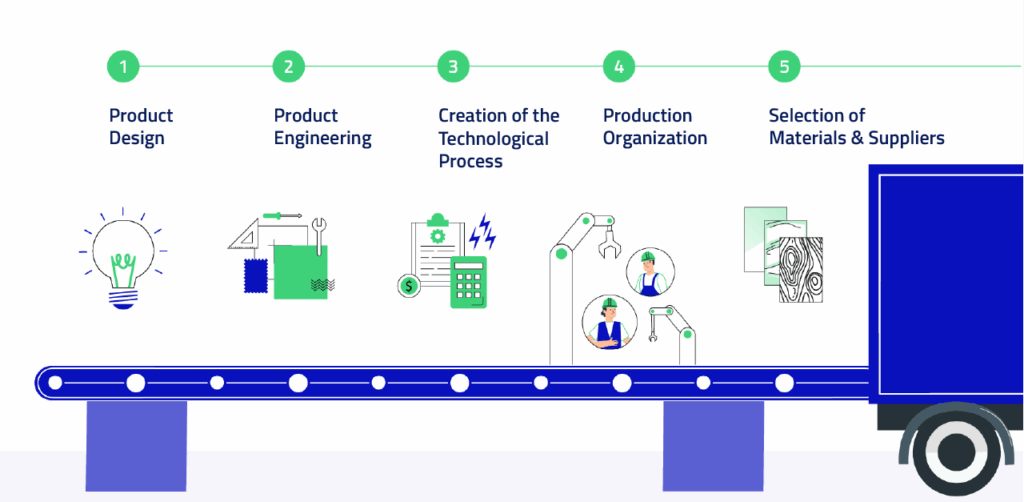
- Product design – creating the concept of a new product for sale.
- Product engineering – determining the final shape of the product and the materials from which it will be made.
- Creating the technological process – defining the manufacturing methods, selecting equipment, calculating labor and energy costs.
- Production organization – arranging equipment and assigning employees.
- Selecting materials and suppliers.
Of course, production management does not end here and extends into the subsequent production work. Each production process therefore includes the following stages:
Stages of Production Management
- Planning
- Organizing
- Directing
- Controlling
The processes within these stages may be based on one of several methods, all of which share the goal of optimization, cost reduction, streamlining activities, and as a result – increasing competitiveness and building a strong, recognizable brand. The outcome of this approach is increased profits, reduced costs, shorter order fulfillment times, higher efficiency, and even improved work quality and employee satisfaction.
Methods of Production Management
The task of people responsible for production management in a company is to answer many questions: what, where, when, how much, and how to produce. This is often not easy, especially in complex processes. That’s why the previously mentioned production management methods and specialized software for manufacturing companies based on these methods come to the rescue.
Today, it is hard to imagine a well-functioning production process that does not operate within a specific system. Popular methods are often based on the experience of leading brands that have perfected their processes. Using their solutions, fully or partially adapted to a company’s specifics, helps achieve goals faster and more effectively.
Here are 4 production management methods worth knowing:
Lean Manufacturing – loosely translated as “lean production”. This method is based on the Toyota Production System. It assumes that the main goal is, on the one hand, maximizing customer value, and on the other – minimizing waste. Waste means overproduction or excessive inventory – actions that consume resources but do not add value for the customer. In simple terms, it is about producing more, better, and faster while using as few resources as possible. One of the main principles of Lean is continuous pursuit of perfection. The customer – their needs, not the company – its capabilities – is at the center of this method.
Kanban – its idea is best captured by the motto “7 × no”: no shortages, no delays, no inventory, no queues, no idle time, no unnecessary operations, no unnecessary movement. Like Lean, Kanban also comes from Toyota. This method enables visualization and control of material flow in the company, as well as tracking the progress of each order. Its goal is to minimize inventory and eliminate overproduction.
MRP System – “Material Requirements Planning”. Its main goal is full control over the production process. It considers product specifications, warehouse stock levels, order progress, and production schedules. The result is constant material availability while keeping inventory as low as possible.
Benchmarking – a technique of systematically comparing company processes with those of the best in the industry. The goal is to find good practices and implement them to improve performance. Benchmarking must be continuous, not one-time.
Lean-based Production Management System – Benefits for the Company
Companies using specific production management models become more flexible and increase their competitiveness. Modern IT technologies, including production management software based on these methods, allow optimization of virtually all processes and better use of machines and workers. Using Nexelem – a system based on Lean Manufacturing – we show how this works in practice.
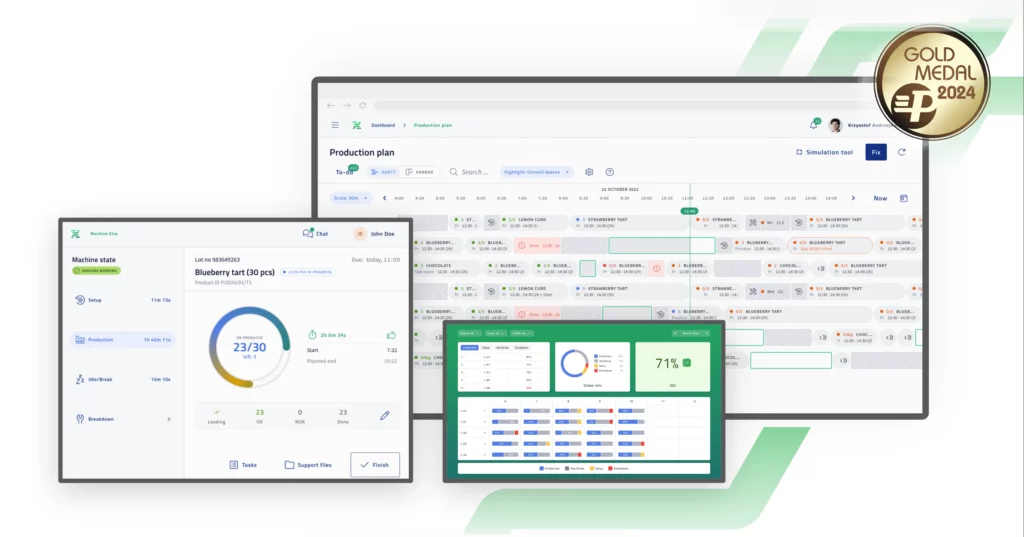
At the production level, Nexelem allows planning production queues on each machine, considering all variables – estimated time, deadlines, and material availability. Batch grouping reduces machine changeover costs. The system also ensures internal logistics flow and provides full reports for data analysis and continuous improvement.
Process optimization also applies to warehouses. Unique codes create structured product catalogs containing stock information and locations. This prevents shortages and surpluses and ensures smooth flow of materials.
Movement of goods and semi-finished products is supported by real-time demand tracking. Nexelem also enables purchase order creation, facilitates receiving deliveries, and manages inter-warehouse transfers.
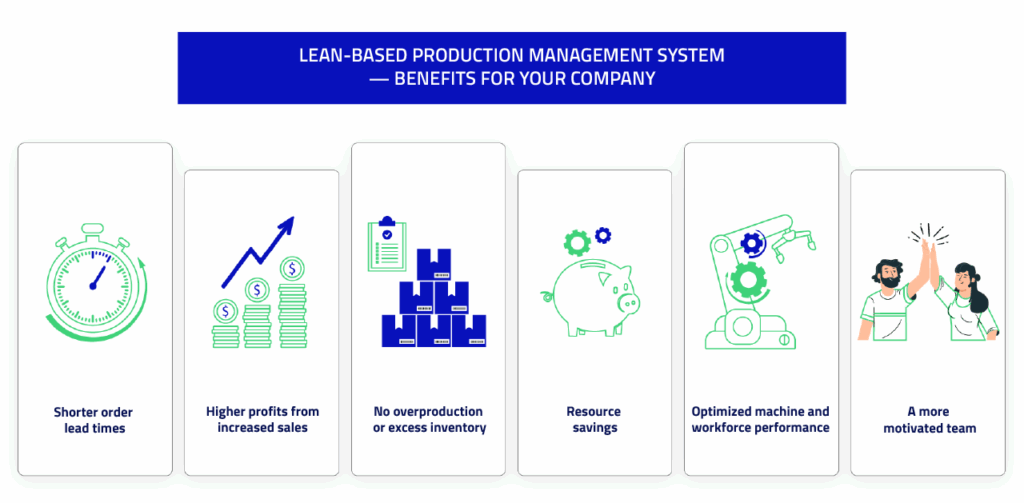
Implementation outcomes
- shorter order fulfillment times
- higher profits due to increased sales
- no overproduction or excess inventory
- resource savings
- optimized work of machines and people
- a more motivated team
Have questions? Contact us!