Generative AI: What It Is and How It Can Transform Smart Factories
Generative AI is fundamentally reshaping smart factories, offering unprecedented capabilities in process optimization, product design, and automation. With its ability to create new data—from text to complex 3D designs—this technology enables rapid prototyping, waste reduction, and dynamic adjustment of production lines to meet current demands. In practice, this translates to shorter lead times, fewer errors, and faster responses to market changes, resulting in real cost savings and a stronger competitive edge.
Table of Contents
- How generative AI differs from traditional AI in smart manufacturing?
- Generative AI in Smart Factories
- Integrating Generative AI with Smart Factory Tools
- Generative AI as Operational Knowledge Assistant on the Shop Floor
- Generative AI: The Next Layer of Intelligence in Smart Factories
- The Future of Manufacturing with Generative AI
You may ask, “What is Generative AI”? Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates new content. It learns from large amounts of data and then produces similar data on its own. In the context of generative AI in manufacturing, this means generating designs, schedules, instructions, or simulations that support daily factory operations. For example, after seeing many pictures, a generative AI model can create a new image that looks like it could belong in the training set. SAP explains that generative AI can “produce text, images, and varied content based on the data it is trained on”.
In simpler terms, it’s like a very smart student who studies thousands of examples and then writes or draws their own story or picture in the same style. In smart manufacturing AI systems, this “student” learns from production data, machine logs, and quality records.
In practice, we build generative AI by using deep learning. OpenAI researchers describe this process:
We first collect a large amount of data in some domain (e.g., think millions of images, sentences, or sounds, etc.) and then train a model to generate data like it.
The network has many parameters, but still fewer than the data points. This forces the model to internalize the essence of the data and learn patterns. Once trained, it can generate new data that follows those patterns. For instance, one can train on a corpus of books and then have the AI generate a paragraph of text that mimics the author’s style. The same principle applies to AI in smart factories, where models learn from historical production data and generate optimized recommendations. It’s a powerful technology that can find many practical applications.
How generative AI differs from traditional AI in smart manufacturing?
- Rule-based vs learning: Traditional AI often follows fixed rules or algorithms to do a task. Generative AI learns from data and creates new outputs. It’s not just following a script – it’s generating something new. This distinction is critical for smart manufacturing AI, where flexibility and adaptation are essential.
- Data types: Unlike simple text chatbots, generative AI can create many kinds of data: text, images, audio, and even videos. For example, it might write a poem, paint a scene, or design a 3D part.
- Beyond prediction: Many AI tools just predict or classify existing data. Generative AI actually imagines new data. SAP notes that it generates new data instances that mimic the input data. This is why it’s useful for tasks like designing or prototyping, not just analysis.
In summary, generative AI is a creative tool. It works by learning patterns in data (images, text, sound) and then it enables generating brand-new examples based on those patterns.
Generative AI in Smart Factories
In a smart factory, we can use generative AI in many helpful ways. At its core, a smart factory uses data and automation to make better decisions. AI in smart manufacturing adds a cognitive layer that supports planning, design, and decision-making across the entire value chain. Generative AI adds a layer of creativity and prediction. For example, it can generate new designs or plans automatically, or analyze problems and suggest fixes.
Examples of generative AI in manufacturing
- Product Design (Generative Design): AI can quickly explore many design options. For instance, Airbus used AI to create thousands of component designs in minutes. Autodesk calls this “generative design,” and it dramatically cuts the time to test new ideas. This is a classic example of generative AI application in manufacturers focused on innovation and lightweight construction. In practice, we give the AI the goals and constraints (like material limits or weight targets), and it proposes optimized designs that we might never have thought of on our own.
- Predictive Maintenance: Generative AI can analyze machine sensor data to predict failures before they happen. By learning from past breakdowns, it can spot subtle signs of wear or anomalies. As part of AI for smart manufacturing, this capability directly reduces downtime and maintenance costs. Google Cloud notes that AI can play a key role in transforming maintenance: it interprets telemetry from equipment to reduce unexpected downtime. If a problem is identified, the AI can even recommend a solution or service plan to fix it. This keeps machines running longer and prevents costly stops.
- Process Optimization: We can use AI to recommend ways to make production lines more efficient. For example, it might suggest rearranging a workflow or changing a schedule based on patterns in the data. Also, gen AI can “recommend ways to make production lines more efficient or less wasteful”. In practice, our planning software Nexelem’s APS module could use AI to generate many optimized production schedules or even compare them based on long-term outcomes of using them by the company.
- Quality Control: Generative AI helps with inspection by producing synthetic training data. Fujitsu reports that Bosch used generative AI to create synthetic images for training vision systems, over 100 times more images than the real data they had. This sped up a project from years to months and improved defect detection quality. In fact, AI can simulate many defect scenarios and train the inspection cameras, making visual checks more accurate.
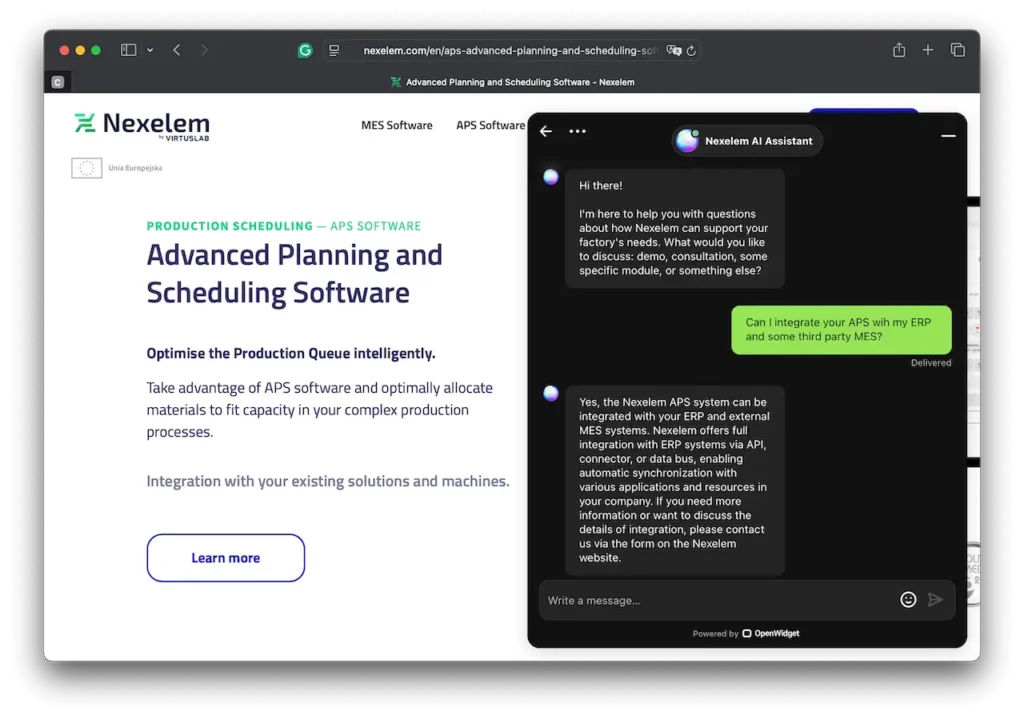
- Customer Support & Documentation: Generative AI can automate paperwork and communication. For example, it can quickly search through product manuals or service documents and summarize the information we need. Google Cloud explains that AI can present instructions in an easy, step-by-step way or synthesize purchase orders to give customers quotes instantly. Even our own AI assistant available on this page works in a very similar way; however, being only a proof of concept, it shows off only a fraction of its capabilities. As a result, technicians get answers faster, and sales teams don’t have to cross-check dozens of documents by hand.
- Robotic and Agent Assistants: In advanced scenarios, multiple AI agents could work together on the factory floor. For instance, we might have a “quality agent” checking products, a “supply agent” ordering materials, and an “orchestration agent” coordinating between them. Fujitsu envisions multi-AI systems where specialized agents handle tasks like production, quality, and distribution, all managed by a controller agent. These agents could use generative AI to adapt plans, generate alerts, or create reports on the fly. A future AI system in manufacturing could have specialized agents for production, quality, and supply chain, all coordinated by an orchestration agent or even its own humanoid robot factory workers powered by the AI.
- Reducing Waste and Costs: By improving every step, generative AI helps the factory meet its goals. It can optimize material use in designs, predict when supplies are needed, and balance production flow. One source notes that generative AI directly supports core smart manufacturing objectives like enhancing efficiency, reducing waste, and responding quickly to changes. In practice, we see this as shorter lead times, lower scrap rates, and faster changeovers when we let AI assist our planning.
According to Deloitte’s 2024 Future of the Digital Customer Experience survey (PDF download), 55% of industrial product manufacturers are currently using generative AI tools in their operations. Even better, more than 40% plan to increase their investment in AI and machine learning over the next three years.
What’s more, one of our VirtusLab clients noticed a 4.4% increase in productivity with ML data analysis. In short, our ML model has made it possible to optimize the manufacturing process and reduce the rate of NG parts in progress.
Integrating Generative AI with Smart Factory Tools
Nexelem is a next-generation production management suite with modules for production scheduling (APS) and manufacturing execution (MES). When combined with AI for smart manufacturing, these systems evolve from execution tools into decision-support platforms. Generative AI can plug into these tools to make them even better fit for the particular factory requirement.
For example, Nexelem’s APS software (production planning module) automates and optimizes production plans. We could use generative AI to compare dozens of alternative production schedules and understand their long-term business outcomes.
In practice, integrating generative AI means we need good data pipelines. The more data our MES collects, the better the AI can learn. But even with our current data, we can start small: ask an AI assistant to review last year’s production logs and suggest schedule tweaks, or have it draft a training document based on equipment manuals. Over time, as we trust the technology more, we can automate larger chunks of work.
Generative AI as Operational Knowledge Assistant on the Shop Floor
From a production management and Lean perspective, one of the most practical applications of generative AI in future factories is the automatic creation of One Point Lessons (OPL). Here, a smart factory AI assistant acts as a knowledge broker, translating MES data into actionable guidance for operators.
By connecting to MES and standard work management tools, a large language model (LLM)-based assistant can generate clear, concise instructions for operators — based on real-time data from the shop floor, such as incidents, corrective actions, or machine setting changes. Instead of engineers or team leaders manually writing training materials, the organization gains a dynamic support system for capturing and standardizing operational knowledge. This significantly reduces reaction time and helps onboard new workers faster, while reinforcing a culture of continuous learning.
Generative AI: The Next Layer of Intelligence in Smart Factories
While humanoid robots are becoming physically capable of replacing humans on the factory floor, generative AI brings the cognitive side of automation — helping machines and systems imagine, optimize, and improve operations continuously. During SuperAI conference, it became clear that generative models will soon support functions like autonomous production planning, dynamic reconfiguration of manufacturing lines, or even real-time creation of digital work instructions tailored to operator skill levels.
Generative AI also has the potential to design new parts and processes on demand. Imagine a factory where the AI, based on changing customer orders and material availability, proposes not just new schedules, but also entirely new part geometries, fixture configurations, or inspection routines — all within minutes. It becomes a creative partner to both engineers and shop-floor teams.
Looking ahead, we may even see AI agents negotiating with each other inside interconnected supply networks — sharing simulated scenarios, optimizing routes, and proposing resilient plans that humans would never consider fast enough. In that world, generative AI won’t just be a backend tool — it will be a key operator in digital industrial ecosystems.
Hint: If you work for a manufacturing company, I would like to invite you to sign up for an online presentation showcasing the capabilities of Nexelm MES/APS.
The Future of Manufacturing with Generative AI
Looking ahead, I see generative AI becoming part of everyday factory work. We’ll have AI collaborators that help us think and create. Just as early factories added sensors and cameras, future factories will add creative AI.
For example, Fujitsu describes how generative AI is evolving into fully autonomous agents that can plan workflows and even take actions toward goals. We might one day say to the factory AI: “Make 100 units of damper X by Friday,” and the AI agents would work together—calling maintenance, ordering parts, scheduling lines—to make it happen. This vision is already being tested: Fujitsu’s “Kozuchi” AI agent can join meetings and suggest actions, and other AI agents can analyze video feeds to improve safety. The next step is production management agents that could handle ordering, quality checks, and distribution. In that world, a generative AI might even write itself a weekly report on production efficiency, or generate schematics for a new part, with minimal human input.
Of course, we need to prepare for this future. That means training ourselves on these tools and updating the infrastructure. Generative AI models require powerful GPUs and fast networks because they process huge datasets. Many companies are investing in high-performance hardware and cloud engineering services to support this. As we upgrade our systems, we should also update our skills. The AI won’t replace skilled workers. It will augment them. Right now, it can handle repetitive or calculation-heavy tasks, freeing us to work on problem-solving and oversight. This addresses real challenges in manufacturing, such as labor shortages and complex production. For instance, one report says generative AI can automate repetitive tasks and even provide personalized training for workers.
Generative AI is a powerful new tool for the manufacturing industry. Despite many imagining it’s not all about text and image generation. It’s like adding a creative analyst to our team. As more examples of generative AI in manufacturing emerge, factories will move beyond automation toward true autonomy. As manufacturers adopt it, they see benefits in design, maintenance, quality, and even internal communication. Many smart factories are already using AI to optimize their lines. I believe that embracing generative AI – alongside systems like Nexelem APS- can make our factories more efficient, agile, and truly innovative. In the future, I imagine checking reports written by an AI assistant, testing out AI-generated prototypes, and having AI plan our next production run.
The future factory will go beyond automation to become truly intelligent.